Introduction. BOOTBLOCK BIOS.
Most of the BIOS firmware currently in use can be called "Firmware with BOOT BLOCK" (BOOTBLOCK BIOS). Such firmware is fundamentally different from earlier BIOSes in that they include an additional section called BOOT BLOCK. Thus, the firmware consists of two parts - the above-mentioned block and the main code (system area - SYSTEM BLOCK). The BOOT BLOCK uses the first 24 kilobytes in the memory chip and contains the information and instructions to be able to initialize the minimum critical system devices, such as , floppy drive and (only some models of ISA cards). The BOOT BLOCK area in the BIOS chip is read-only and can only be reprogrammed using flash utilities using special commands. This area can only be present in those BIOSes that have a size of 256 kilobytes (2 megabits) and it allows you to recover a BIOS damaged during its update. In a 1-megabit BIOS, there is simply nowhere to fit such an area, so it can only be restored using the "Hot Swap" procedure (we will discuss it below) or firmware on the chip programmer. The procedure for flashing the BIOS (the operation of the program - the flash driver) can be divided into several stages:
- Program download and chip identification flash memory(programming size and voltage)
- Board Chipset and Type Identification
- Verifying the checksum of the new firmware.
- Erase the main area in the flash BIOS chip (filling with zeros). BOOT BLOCK is not affected.
- Overwriting the main area with the new BIOS code.
- Load BIOS variables to default values and restart the computer.
AWARD BootBlock BIOS v x.xx
CMOS checksum error
At this point, the system will attempt to boot from the system floppy to attempt a BIOS recovery. Below we will consider the BIOS recovery methods.
BIOS recovery methods. There are several methods:
- Using BOOT BLOCK to Flash BIOS
- Using the hot swap method
- Chip firmware on the programmer.
- Buying a new chip with the required firmware.
We already know that Board BIOS that have a BOOTBLOCK section can be restored from floppy if the BOOTBLOCK itself is intact. Computers that have a corrupted AMI BIOS boot up will not display anything on the screen, but the floppy drive indicator (FDD) will light up and the system will attempt to read from the disk. The BIOS recovery procedure loaded from the BOOT BLOCK will attempt to find a file on the floppy disk called AMIBOOT.ROM, and if such a file is found, it will be written to the BIOS system area. It is important that your computer has a working system speaker connected to , because at the end of the BIOS recovery procedure, the system will indicate this with four beeps. Thus, to recover a damaged AMI BIOS, do the following:
- Format a reliable (quality) floppy disk 1.44 mb
- Copy the BIOS firmware suitable for your board to it. Many firmware available on the Internet are posted there in archived form. Naturally, the archive must be unpacked and copied the unpacked firmware.
- Rename this file to AMIBOOT.ROM
- Turn on the computer and insert the prepared floppy disk into drive A:
- After about 3-4 minutes, the system should notify you with four beeps that the flashing procedure has been completed. Remove the diskette. The computer should restart.
Recovery AWARD BOOTBLOCK BIOS.
In the case of the AWARD BIOS, the procedure is similar, but there are differences. You will need to prepare a working diskette with the BIOS firmware in *.BIN format, write the flasher program and the AUTOEXEC.BAT file to the diskette. AWARD BOOT BLOCK cannot automatically restore the BIOS system area, so you will need to write BIOS flashing commands to the AUTOEXEC.BAT file. The system will run this BAT file and thus flash the BIOS system area. The recovery procedure looks like this:
- Create a boot disk. To do this, it is best to issue the FORMAT A command from the DOS command line: /S The /S switch means that system files. If you are using WindowsME, WinNT, Win2000 or older systems, this method of creating a floppy disk is not available to you. Go to www.bootdisk.com and download the boot disk image from there.
- Copy the desired BIOS file to the floppy disk. Many firmware available on the Internet are posted there in archived form. Naturally, the archive must be unpacked and copied the unpacked firmware. Copy the flash driver there.
- Using a text editor (for example, Notepad) or any editor built into DOS command shells (Norton commander, Dos navigator), create the AUTOEXEC.BAT file on the floppy disk. The file must be in text format, and its name must exactly match the specified one, without the slightest variation . If you are using Notepad? then you may need to change the file extension from TXT to BAT
- In the same text editor paste and save the following lines in a file:
@ECHO OFF
@AWDFLASH BIOSFILE.BIN /py
The /py key is needed in order for the firmware procedure to start without user intervention. The names AWDFLASH and BIOSFILE.BIN are given here as an example, they should be replaced with the name of the flash driver and the file name with the firmware. It is also advisable to check if your flasher program with the /py key actually starts the automatic flashing procedure, because despite the standards, the commands may differ. To check, run your flash driver with the /? key. For example, like this: AWDFLASH /? - Insert the prepared floppy disk into the drive and turn on the computer. The computer should boot from the floppy disk, run the above commands, and restore the BIOS. If the procedure went well, the computer will restart and start up as usual. The floppy disk must be removed from the drive, of course. If the BIOS recovery does not work, see the Troubleshooting section below.
This technique involves removing the BIOS chip from one board (from a board that is not working due to a failed flashing) and installing this chip into a healthy board while it is functioning (in standby state). This technique is very risky because you will have to take out a normal BIOS chip and put in a chip with corrupted firmware while the board is energized. Moreover, you risk damaging not only both microcircuits, but also, and in especially unsuccessful cases, the entire system. There is also a risk of electric shock to the operator performing this procedure.
This procedure requires that you have two computers with the same types of BIOS (AWARD or AMI) and the same types of their chips. It consists in the following:
- Start the working computer you will be using for recovery and boot into the DOS prompt (DOS prompt). Make sure you don't have any resident programs loaded.
- Carefully remove the BIOS chip from the running machine. Remember how it was installed there so that you can install it the same way later. Beforehand, you can practice removing the chip on a turned off computer so that the procedure goes quickly and confidently. Try to have all the pins of the microcircuit disconnected from the connector at the same time.
- Insert the chip containing the corrupted BIOS into a working computer. Make sure that the key on the chip matches the key on the connector to prevent incorrect installation of the chips! If you insert the chip incorrectly, when you turn on the computer, it will definitely be damaged! Again, practice doing this ahead of time with the car turned off. Try to ensure that all the pins of the microcircuit are inserted at the same time.
- Run the BIOS programming utility and flash the chip with the correct firmware required for the first (currently non-working) computer. If you receive a warning about a chipset type and/or board name mismatch, ignore it. If the flasher does not allow you to ignore this warning, and this is an AMI BIOS, then run the program with the /x key to enter the program's graphical interface and flash manually. In other cases, try running the flash driver with the /? and find out which key can help to ignore the warnings.
- After flashing the BIOS, turn off the computer, carefully remove the programmed chip, and place each of the chips in its place. Make sure that the key on the chip matches the key on the connector to prevent incorrect installation of the chips! If you insert the chip incorrectly, when you turn on the computer, it will definitely be damaged!
- Turn on your computer. If the procedure went well, its launch will look as usual. If the BIOS recovery does not work, see the Troubleshooting section below.
Problem: After following these instructions, the system still does not boot normally and all it does is access the disk drive.
Possible Solution: This situation means that the firmware procedure was completed unsuccessfully. There are two most likely causes: an incorrectly selected firmware or a faulty BIOS chip. In the first case, you can try to repeat the BIOS recovery procedure. In the second case, you will have to purchase a new chip and flash it on the programmer.
Problem: After restarting the computer gave the message "CMOS Checksum bad" and "Press F1 to Enter Setup"
Possible Solution: This is generally not a problem. The fact is that after updating the BIOS, the values \u200b\u200bof the variables set in BIOS Setup are arbitrary. You need to go into BIOS Setup, load the default variables (commands load system defaults, load optimal settings and the like) and then, if necessary, fine-tune the BIOS "to your needs".
Problem: During the AWARD BIOS recovery process, the system starts reading from the floppy, then stops and nothing else happens. When the computer is restarted, the situation repeats itself.
Possible Solution: This situation most likely indicates a problem with the floppy disk or drive. Check on another computer that the disk is bootable, that it contains the AUTOEXEC.BAT file, the BIOS programming utility, and the firmware itself, and that the AUTOEXEC file has the correct contents. If you can see the boot process on the screen and the system boots into the DOS prompt, then try manually entering the BIOS flashing commands and watch for error messages. Also try using a different firmware utility and a different BIOS firmware file. If the floppy is fully functional, try replacing the floppy drive.
I had to face the fact that I damaged ami bios on one of the old computers. I often had to flash bios, but this was the first time I "broke" it. There is a lot of information on the Internet about how to restore it, but it did not help me. As it turned out later, not everything that needs to be done is written there in order for the resuscitation to be successful or to begin at all.
A little intro. BOOTBLOCK
Almost all modern BIOSes have BOOTBLOCK - a special section of memory for system recovery. This section contains instructions and information for initializing a minimum of critical devices.
Preparing for recovery
Very important information, which I did not find at all in my search for a solution to the problem. Necessary disconnect all devices unnecessary for BIOS recovery from motherboard.
What no need: mouse, all usb devices, hard drives, optical drives, PCI devices, video card, and so on. I even needed to remove one bar on one of the computers (and leave one) random access memory.
What necessary: floppy drive, keyboard, RAM and processor.
BIOS recovery
- Format floppy disk and write a file with the required BIOS version there
- Rename it to AMIBOOT.ROM
- Be sure to turn off your computer and not just turn it off via the POWER button
- Press key combination CTRL+HOME
- Turn on the computer and do not release the key combination until the system starts reading information from the floppy disk
- Wait. At the end, the computer will either give 4 short beeps or “do not say anything” at all and reboot itself
If everything went smoothly, then good. There may be problems, for example 5 short beeps - the system cannot read the file.
Full list of signals during AMI BIOS recovery:
| Number of beeps | Index |
|---|---|
| 1 | Media not defined |
| 2 | ROM file not found in root directory |
| 3 | Insert the next media volume |
| 4 | Flash programming completed successfully |
| 5 | File read error |
| 7 | Flash EPROM not defined |
| 10 | Error when erasing flash memory |
| 11 | Flash program error |
| 12 | ROM file size problem |
| 13 | ROM image does not meet BIOS requirements |
I hope the information will be useful to someone.
Guess the riddle: it stands like a beehive buzzes. But there is no smoke coming from the chimney, because this is not a native factory, but a computer on which the BIOS is damaged. And he buzzes because that's the only thing he is now capable of. Without a bios, it's just a bunch of lifeless iron. Is this worth worrying about? Of course not. After all, now you have a great bedside table!
The system unit as a bedside table? Well, I do not! We know how to make it work. Today we'll talk about how to restore the BIOS if it crashed.
What causes BIOS flashing
The BIOS and its "descendant" UEFI, which modern motherboards are flashed with, are special computer programs required for initial setup and management of PC devices until the operating system starts. They are stored in special flash memory chips on the motherboard, one of which is shown in the picture above. It seems to be a good storage place, reliable, but sometimes the BIOS gets uncomfortable there and runs away. More precisely, it is damaged and ceases to perform its tasks.

There are not too many reasons for BIOS damage, in some cases they are obvious, in others they are not. Here is a list of the most common:
- The computer's power went out while updating the BIOS.
- The flasher program (flasher) incorrectly interacts with the firmware or flash memory chip.
- Flashed a BIOS version that does not match this motherboard. Yes, for each model and revision of the "mother" it has its own.
- If the update is carried out from under a working operating system- system failure or software interference, for example, blocking by antivirus.
- Incorrect user actions, for example, restarting the computer before the update is installed.
- Failure of the flash memory chip.
- Hidden BIOS microprogram errors. Sometimes this explains spontaneous "gatherings" that occur for no apparent reason.
- Electrical failure of the motherboard.
How BIOS corruption manifests itself
In most cases, the BIOS firmware is partially damaged, so the symptoms of a failure can be different:
- When you press the PC power button, only the cooler turns on, which immediately starts to rotate at maximum speed. Sometimes the LED indicators on the case and keyboard light up.
- One or more seconds after power on, a cyclic reboot begins. Outwardly, this is manifested by a cycle of spin-ups and stops of the cooler, which are repeated as long as power is supplied.
- When turned on, the power indicator lights up, the cooler does not spin.
- The computer shows no signs of life. This happens when the boot block, the BIOS bootloader, is damaged. This is the hardest case.
There is no image on the screen. Even the splash screen of the manufacturer does not appear.

There are other forms of damage to the BIOS, more precisely, its area, which stores the configuration of the ME controller (an integral part of the chipset) on boards that work with Intel processors– the so-called ME-region. If there is a problem in this area, a computer or laptop may:
- Incorrect loading or not turning on at all.
- Shut down or restart after equal intervals time.
- It is incorrect to regulate the cooler rotation speed, for example, to turn it at high speed regardless of the load.
The elimination of such failures consists in reading the BIOS dump, replacing the ME region with a clean one and re-flashing it using the programmer. Since this is usually done by repairmen, and not by computer owners, we will not dwell on this. Let's better do what can be done at home without special equipment and the risk of finally sending your "iron pet" to the realm of eternity.
BIOS recovery without a programmer is possible only if the bootloader is saved. It is sometimes possible to determine whether it has been preserved or not by indirect signs: flashing of the screen backlight, sound signals from the system speaker, the reaction of the motherboard to turning on without RAM (sound or flashing of indicators), etc. If the BIOS bootloader is preserved, the first moments of the computer work normally, the failure appears a little later.
How to restore the performance of a motherboard with a failed BIOS
Asus
Many Asus brand desktop motherboards support the technology USB flashback, which is designed to quickly update and restore the BIOS in the event of a failure. This does not require anything other than a USB flash drive with a capacity of up to 4-16 GB and the BIOS file itself, which must be downloaded from the manufacturer's website from the section about your "mother" model.
After downloading the firmware, you need to rename it. For example, the file "Sabertooth X79" (model name) is renamed to "SABERX79.ROM", the file "Sabertooth Z77" to "Z77ST.CAP". Information on how the firmware file should be named for your model is most likely on the Asus website, but if you do not find it, check on the forums or in support.
Next, save the renamed BIOS to a FAT32-formatted flash drive and plug it into the USB port marked " flashback" or " ROG Connect". It is advisable to turn off the computer before this, this will increase the chance of a successful recovery.

After connecting the flash drive, turn on the PC and press the " BIOS". Hold it down for about 3 seconds until the indicator light on the board starts blinking. Blinking indicates that the file was successfully read and flashed into memory. When the flashing process is completed, the indicator will turn off.
If your board is from a budget segment or not too new, that is, it does not support USB Flashback, most likely you can restore it in another way. If the computer is equipped with a floppy drive or optical drive, write the renamed BIOS file to the root directory of a blank floppy disk or CD, place it in the drive, turn off and then turn on the PC. The firmware will be completed when the drive indicator turns off. If there is no drive, use a USB flash drive.
gigabyte
On Gigabyte boards with Dual (dual) BIOS, failures rarely occur, since in case of damage to the firmware in the main chip ( M ain_ BIOS) the dump from the backup is copied into it ( B backup_ BIOS). As long as the main flash memory is healthy and contains firmware, even damaged, the board remains operational.
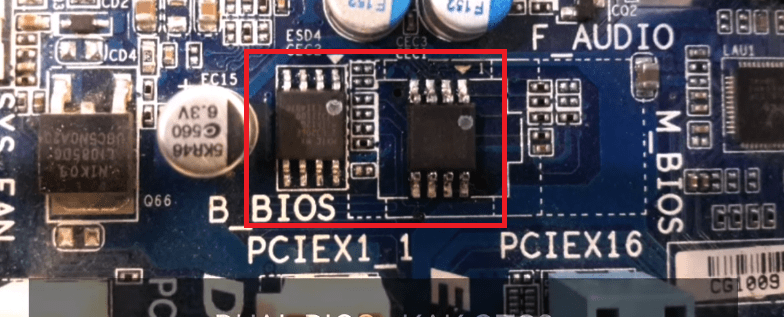
Problems with starting a board with Dual_BIOS are possible in the following cases:
- The main chip is missing or has failed.
- The microcode in the main chip is completely erased.
- The contents of both chips are damaged.
Some Gigabyte "mothers" can boot from backup flash memory and use it as the main one. Another group of boards from this manufacturer uses a dedicated area on the hard disk as a BIOS backup medium. This is a less reliable option, but still better than nothing.
Restoring the Gigabyte BIOS from a backup is usually done automatically, but if this does not happen, try unplugging the computer, wait a bit and turn it on again.
MSI and others
Most Micro-Star motherboards use a firmware recovery technology very similar to ASUS's - using a flash drive, floppy disk or CD. Copy the BIOS to blank media, connect it to the PC, press the shutdown button for 4 seconds, hold down the combination on the keyboard leftctrl +Home(or Alt +ctrl +Home) and, without releasing the keys, turn on the computer. The beginning of the firmware process can be judged by the blinking of the flash drive or drive indicator.

BIOS on MSI board. On the right is the JSPI1 port for firmware on the programmer
On MSI motherboards and some other brands that are more than 8-10 years old, the BIOS is flashed from a floppy disk. The instructions for AWARD and AMI BIOS are slightly different.
To restore the AMI BIOS, do the following:
- Rename the BIOS file downloaded from the motherboard manufacturer's website to AMIBOOT.ROM.
- Move it to the root of a clean floppy disk. Insert the floppy disk into the drive of the switched off PC.
- Press left Ctrl + Home on your keyboard and turn on your computer.
To restore the AWARD BIOS:
- Place the flash driver and BIOS files on a floppy disk (usually downloaded in one archive).
- Create a text document on a floppy disk containing the name of the BIOS file with the extension bin. Rename the document to autoexec.bat.
- The next steps are the same as above.
By the way, some motherboard manufacturers post BIOSes on their websites only in exe format - in one bottle with the flash driver for updating from under Windows. Sometimes such a file can be unpacked as an archive, but users often do not understand what exactly of its contents is the firmware. There is no universal solution for such problems. In order not to aggravate the problem, it is better to consult on the specialized forums or in the technical support of the manufacturer.

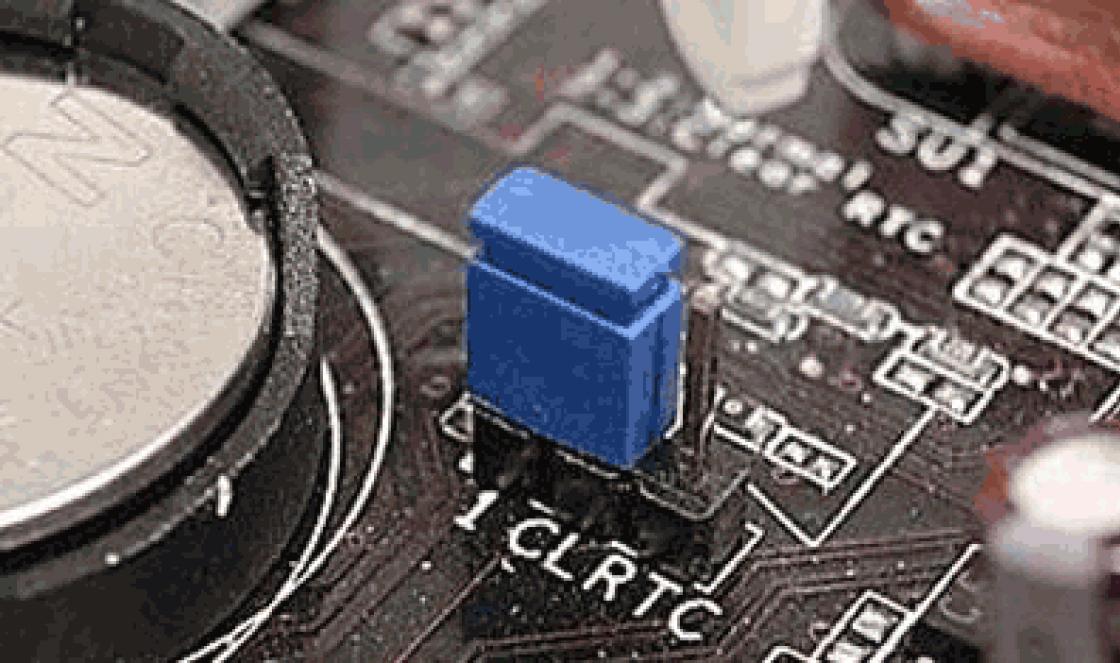
On some boards, before restoring the BIOS, you also need to remove the real-time clock (RTC) battery from the socket or rearrange (remove) the clear CMOS jumper. It is important to find out these points before starting the procedure.
Features of BIOS recovery on laptops
On laptops, as well as on Gigabyte boards, the BIOS is also often stored in two flash memory chips. But it's not Dual and it has no backups. Both chips contain different parts of the firmware, or one contains the main BIOS, and the other contains the multicontroller program. To prevent the device from turning on, it is enough to damage the microcode in at least one of them.

The procedure for recovering a crashed BIOS on laptops is about the same as on desktops. The firmware file downloaded from the manufacturer’s website and the flasher program (the latter is not always needed) are placed on a clean USB flash drive formatted in FAT32 / 16, connected to a de-energized device (simply turning off the laptop is sometimes not enough, you need to disconnect the power supply and remove the battery), insert a charged the battery in place, turn on the device and hold down the key combination. On different laptops, different keyboard shortcuts are used for this, for example:
- Ctrl (left only or both) + Home
- Windows + B (this and other letters are given in the Latin layout)
- Windows+F
- Windows+M
- Windows + Esc
- Fn+B
- Fn+F
- Fn+M
- Fn + Esc.
The main work is to unpack and rename the BIOS files. Again, there is no single rule here. In most cases, you have to get the firmware from exe files, but! Many manufacturers include BIOSes for different revisions of one platform or a whole series of platforms in the program, and it can be very difficult to choose the only file you need from them. In order not to be mistaken, read the instructions for the firmware of your particular model and platform revision on the specialized forums. And feel free to ask questions.
I deliberately do not provide instructions in the article for restoring BIOSes by flashing on a programmer with and without soldering, closing various contacts, hot-swapping removable flash memory, etc., since all these methods are unsafe and require certain knowledge. However, among the readers, there are probably those who have done something similar on their PC and got good results. It will be great if you describe in detail your actions in the comments to the article. Also, stories about negative experiences are welcome so that other readers can avoid mistakes thanks to you. In the comments, be sure to include the model name and revision of your motherboard, as well as BIOS version with which you were working.
BIOS was created in 1975, its abbreviation stands for Basic Input/Output System, and its main function is to run the operating system and PC hardware components. It also loads power and temperature management features. The firmware identifies, tests and starts the main components of the system, such as HDD, video card and keyboard.
Most modern computers store the BIOS on a ROM chip on the motherboard. If it has crashed, then, as a rule, determining the model of the motherboard will help restore the BIOS. This will depend on the firmware restart.
Restoring the BIOS is a simple process that anyone can carry out on a PC if there is a serious problem with it and you need to return the settings to the factory state. Before restoring the BIOS, the act of resetting the motherboard is performed, the process is called Clear CMOS. It provides for the following actions:
- clearing the parameters stored in the BIOS ROM;
- returning the PC to a neutral state from which it starts;
- Troubleshooting crashes when starting the PC for the first time after assembly or after updating the BIOS.
The main reasons for performing firmware recovery:
- The motherboard does not start up after configuring BIOS-specific settings.
- One of the most common reasons is manual setting RAM on the motherboard. If a parameter is mistakenly entered from the many settings that the RAM has, the board will fail and the PC will not start.
- Another of the most common reasons is overclocking. If the user raises the frequency, while not having enough Vcore for the processor, it is very likely that the motherboard will not boot.
In order to reboot, you need a key typed on the keyboard. It differs for different computer models and is usually indicated on the screen when starting the PC, for a short period of time. Before restoring a BIOS that has crashed, you need to find out the key keys.
They can be: F1, F2, F10, F11, F12, Esc or some other combination like "Control + Alt + Escape". If the user does not know the recovery key and does not see the indication on the screen, then a query for the phrase "computer brand + enter BIOS" should suggest a solution. The same answer is in the PC manual. After the correct set of keys, the user will see the BIOS setup screen.

If the BIOS has flown, but how to restore on a PC, the user does not know it, experts recommend performing Clear CMOS. To do this, the first thing you need to find on the surface of the motherboard is three grouped contacts, next to which are the phrases Clear CMOS or CLR_CMOS. It will be easier for the user to find the mode if he first reads the motherboard manual. There will be a jumper on these pins that closes the contact between them. It should also be noted that there are those that have only two contacts, without any jumper.
The mode execution algorithm is as follows:
- Turn off the computer.
- Find the battery on the motherboard. This is a round battery, similar to an element from an electronic wrist watch, located on the surface of the board.
- Carefully remove it from the outlet where it is located.
- Before restoring the BIOS, which has flown, change the position of the jumper, which closes the circuit between the two contacts. If contacts 1 and 2 are initially closed, then set the position so that contacts 2 and 3 close.
- Find a conductive metal surface and manually close the circuit between the two contacts. A flathead screwdriver is an excellent choice for this purpose.
- After completing this step, leave the circuit closed for at least 30 seconds.
- After this time, perform the same actions, but in reverse order.
- If everything went correctly, the system will start with the default BIOS settings.

If the BIOS on the PC has crashed, and the user does not know how to restore it and cannot guarantee the safety of the machine, then it is better to perform a full firmware reset on the laptop.
The algorithm of operations is as follows:
- Turn on the computer and study the BIOS splash screen, which will appear at the very beginning and tell you which function key (F2 / F8) you need to press to access the configuration.
- Press and hold this key until the setting screen appears.
- If a timely press opportunity is missed, the PC will continue to boot from Win in normal mode, and a reboot with repetition of the steps will be required.
- After successfully entering the BIOS setup screen, use the function and scroll keys to navigate through the menus.
- Find the "factory reset" option.
- If Windows has crashed, as a rule, following the instructions on the screen will help restore the BIOS to return to the original configuration.
- Confirm your choice and close the screen.
- Because the BIOS is in ROM, it must have a constant power source to store any changes that are made to it each time the computer is disconnected from AC power.
- If it is not possible to return to the factory settings, turn off the power from the BIOS, it returns to its original configuration. The process consists of disconnecting a small motherboard battery. In many laptops, the BIOS battery is easily accessible and is located at the bottom of the device.
- It doesn’t matter how the BIOS on the computer crashed, updating the motherboard SMOS will help restore it correctly. To do this, you will need to remove the battery and, by touching a metal object, ground it.
- Next, remove all the screws that hold the battery cover in place.
- They find the BIOS battery in the form of a small lithium structure, similar to a watch battery, remove it, trying not to damage neighboring circuits. They wait for a minute for it to discharge, and insert it into place. Then repeat the starting procedure from the beginning.

The main problem when updating the BIOS in Windows 10 can occur when trying to reboot. Sometimes the user cannot open the BIOS no matter how many key presses. This is because Windows does not restart the PC by default.
If Windows 10 has crashed, the following algorithm will tell you how to restore BIOS through the use of key keys:
- In order to be able to enter the BIOS, the first thing to do is to start booting the PC.
- To turn off the computer, press "Alt + F4" on the desktop or use the Start menu. It must be borne in mind that if the laptop uses "quick start" technology, it is quite possible that a normal BIOS shutdown will not start. A number of preliminary steps need to be taken.
- First click on the "Start" menu and then select "Settings".
- In the Windows configuration, go to the last section called "Update and security", where there are similar recovery configurations and troubleshooting.
- Click on the "Recovery" tab in the panel on the left, and then the "Restart Now" button in the "Advanced Startup" section.
- A menu will appear with a blue background which is used to solve problems with Windows and one option is to enter BIOS.
If Windows 10 crashed, how to restore the operating system through BIOS, users will be prompted by the special tabs "Solve problems" and "Advanced options".

Gigabyte motherboards include a feature called "dual BIOS" that allows if a gigabyte BIOS update fails or loses power during the process, a defective BIOS can be restored. Reserve copy. It doesn't matter how the BIOS crashed, it will be possible to restore work on the Gigabyte dual only using the update.
Updating BIOS gigabytes from Windows can be done in two ways:
- after loading the BIOS from the motherboard;
- update the BIOS from the Gigabyte server so that the program looks for the latest version.
If this needs to be done using a previous BIOS download, for example, when there is no Internet on the PC, download the above program and the BIOS version that is needed. The latter is recommended to keep the hardware running at the best possible performance and stability.
You can make a backup copy that is currently available by clicking the "Save current BIOS to file" tab and specify the route to save the file. Once the user has everything he needs, he proceeds to update by clicking on the "Update BIOS from file" tab, the program will ask you to search for a previously downloaded file.
Q-FLASH application
It is possible to update from the Gigabyte's own BIOS, with an application called Q-FLASH built into it. Before starting, format usb to fat32 and unpack the BIOS inside. Insert into port USB before entering the PC. The utility offers 3 options: the first one is "Update BIOS from disk", the second one is "Save BIOS to disk", and the third one is "Quit Q-" to exit the application.
After the BIOS has flown, the use of a special utility will help restore the functionality of the operating system step by step.
The algorithm of actions looks like this:
- Select the usb which contains the bios file.
- Select the BIOS version to enter and start the update process.
- Perform a check for a new file inside usb.
- The assistant asks to the version that is in usb, confirm "yes", and the process begins.
- Make sure the process is done correctly.
- Perform a reboot, enter the BIOS and check that the version has been changed.
This process allows you to upgrade your gigabyte BIOS to a higher or lower version. In addition, with Gigabyte's dual Bios system, you can be calm in front of possible failures, because they start the system with its backup.

You can restore the system without going into Windows 7. It often happens that after "Windows 7", restoring the system through BIOS is the only way to restore the PC's performance. The procedure will depend on the specific equipment installed on the machine. If the device has a CD / DVD player, remove all discs from it. Then turn off the computer and external USB drives.
Recovery algorithm:
- Turn on the PC and quickly press the F8 key on the keyboard. The Win logo should not be displayed. It is best to press F8 several times in a row, at the time of starting the PC.
- When the process goes well, a screen appears with a black background and white letters. Enable advanced OS boot options by using the arrow keys to select the one that installs safe mode from command line, and confirm Enter on the keyboard to enter it.
- After downloading a series of files, an MS-Dos console window opens with a black background and white letters. Write the command: rstrui.exe and press Enter on the keyboard.
- The recovery assistant starts, the user must follow all its instructions.

Surftec reinstalls all Lenovo systems to stock Windows version 7 Professional, while new systems usually install with Windows 8 or 10.
Windows 8 supports a newer, faster BIOS - UEFI, which provides additional security. For Windows startup 7 this mode should be disabled. For the situation when the BIOS crashed on lenovo laptop, to restore its performance will help to establish the causes of the emergency.
If the user has reset the BIOS and the default features have been enabled, then Windows 7 will most likely not be able to start automatically. There may be other problems in the system, such as a broken wireless connection or old hardware drivers, which will also interfere with the normal recovery process.
- Close the windows and make sure that the laptop is completely turned off, to do this, go to the "Start" menu and select "Shut down".
- Press the power button and then the F1 key every two seconds until the BIOS welcome screen appears.
- Navigation through the BIOS is done using the arrow keys on the keyboard. The left and right keys move between the top BIOS headings "Main", "Config", "Date/Time", "Security", "Startup" and "Restart".
- The up and down arrows navigate through the available options on each page.
- The enter or return key will open the option with additional settings, then use the up and down arrows to highlight the desired option, and the backspace and enter keys.
- Use the right arrow key on the keyboard to select the "Reboot" screen.
- Use the down arrow key to select the OS Optimized Defaults option.
- Press the return or enter key, a pop-up window will appear.
- Use the up and down arrow keys to select Disabled. The selected option is shown in bold and white text.
- Use the up arrow once to select "Load Setup Defaults" and press the "Return" or "Enter" key.
- Make sure "Yes" is selected using the left and right arrow keys, and then press the "Enter" key. The selected option is highlighted with a black background.
- Press the F10 key and use the left and right arrow keys to select Yes.
- Press the return or enter key to select "Yes", now the machine will save the new settings and reboot.
AMI Biostar Boot Software
If the BIOS has crashed, how to restore the biostar from the floppy disk of the boot block can be clarified in the technical documentation for the motherboard. But since this scheme is used for old modifications of computers or PCs operating in server mode, the instruction may have been lost, then you will have to look for a topic on the Internet.
This setting is a standard feature of the AMIBIOS8 kernel, enabled by default, and allows the user to restore the BIOS image using a floppy disk without the need for additional utilities. Before restoring the biostar, if the BIOS has crashed, follow the following instructions. Instructions for manually starting the recovery of the boot block from a floppy disk are as follows:
- Insert the floppy disk containing the new BIOS file into the root directory of drive A. In most cases, the file should be named AMIBOOT.ROM. However, this filename may differ from one product to another. The user can clarify this information in the technical documentation of the motherboard.
- Press and hold the keys while turning on the power until the floppy drive access indicator lights up, which may take a few seconds.
- The keys are released and AMIBIOS emits a series of beep codes that indicate that the system ROM BIOS file is being updated.
- After the file is loaded, a progress dialog box will be displayed on the screen.
- After successfully programming the flash ROM, the computer will restart.
- The user should not interrupt the BIOS flashing process until it is completely completed.
- One of the functions of the AMI BIOS boot block is a code to check the integrity of the BIOS image in flash memory.
- If a problem with the BIOS image is found in the boot block code, boot block recovery will automatically begin. This condition will be indicated by a series of beep codes.

BIOS Recovery Boot Block is a special BIOS boot block with minimal initialization. The function is enabled to restore the firmware to successfully complete after the BIOS flashing process has failed. The system provides "Fn + Esc" hotkeys that enable the process of restoring a working system during BIOS POST. It is recommended to use the AC adapter and battery to use the function. When enabled, the BIOS will force you to enter a special block called the Boot Block.
Steps to restore using a USB flash drive should be taken:
- Pre-prepare the Crisis USB key. It is created by running the Crisis Disk software on another Windows system.
- Connect the USB disk.
- Run the wincris.exe program to create a Crisis USB disk.
- Click "Start" to start the process.
- Select the "Quick Format" option for the disk and click "Start".
- Follow the on-screen instructions to create a disc.
- Copy the BIOS file KAYF0X64.fd to the root directory of the USB flash drive.
- Connect the USB storage device to the USB port.
- Press the "Fn + ESC" buttons, turn on the power.
- The power button blinks orange once.
- Press the power button to start the Crisis system mode.
- After CRISIS completes, the system reboots with a working BIOS.
Acer reset options
If the user has forgotten the BIOS password for an Acer laptop, they will need to access the BIOS in order to make some hardware changes to the computer, which may be password protected. Resetting it before logging into Acer is easy.
The procedure for resetting the password through Acer eSettings is as follows:
- Install the Acer Empowering Technology software.
- Open the Start menu and select All Programs > Empowering Technology > Manage with eSettings.
- Click "BIOS Passwords" on the footer of the screen.
- Using the Create or Delete options, control is restored.
- Reset Acer laptop password.
Removing it with a CMOS battery is the common way. This method involves the use of computer equipment, therefore it is intended for users who know the PC device.
It doesn’t matter how the BIOS crashed on an Acer laptop, you can restore the laptop using the firmware method:
- Disconnect the power cable from the PC.
- Remove the computer case with a screwdriver and find a flat, round and metal CMOS battery.
- Learn how the latches hold it in place in order to properly remove the CMOS battery.
- After extraction, wait 30-40 seconds, put the battery back in place and restart the PC.
- If everything went well, the password should no longer exist.
Thus, BIOS is a basic input-output system, an indispensable function of the operating system of hardware components, the correct operation of which depends on the reliability of the computer. He does not like to interfere with his settings often, but nevertheless, a competent user needs to know how to properly work with the system for any extreme cases.